OIDC authentication¶
OpenID Connect (OIDC) is an identity authentication protocol built on top of the OAuth 2.0 framework. OIDC is designed to verify user identities and provide authentication, ensuring that users are who they claim to be. OAuth 2.0 is used for user authorization to access resources.
With the OIDC / OAuth 2.0 support in Percona Server for MongoDB, users can authenticate and authorize in your infrastructure without sharing their credentials. To make this happen, you enable a single sign-on (SSO) for Percona Server for MongoDB. SSO requires an external identity provider (IdP).
The IdP is a centralized place to authenticate and authorize humans and applications to access multiple resources in your infrastructure. User credentials and access policies are stored centralized on the IdP side. You can configure different access policies and tailor permissions for a group of users of a specific user.
Percona Server for MongoDB stores user roles in the format <authNamePrefix>/<authorizationClaim> that control access to the database resources.
Currently, Percona Server for MongoDB supports Okta external identity provider. We plan to extend the list of supported external identity providers in future releases.
Authentication workflow¶
Percona Server for MongoDB supports two authentication workflows with OIDC:
-
Authorization code with Proof Key for Code Exchange (PKCE): A MongoDB client (for example,
mongoshor Compass) opens a browser and redirects a user to the login portal of an external identity provider to pass authentication. This is the default authentication workflow. -
Device authentication: instead of redirecting a user to authenticate on a login portal directly, a MongoDB client receives the URL of the login portal and the authentication code. The user follows the URL and enters the authentication code. The example use case for such a workflow is when both a MongoDB client and Percona Server for MongoDB run in an environment that has no web browser such as a Docker container or a cloud infrastructure.
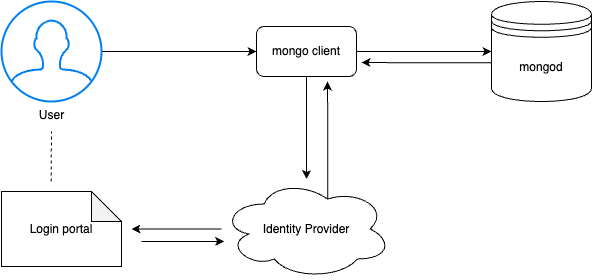
The following diagram illustrates the authentication flow.
- A user connects to Percona Server for MongoDB using a MongoDB client. The client must support OIDC.
- The MongoDB client requests authentication from the external identity provider (IdP).
- The IdP generates the authorization code. A user is redirected to the login portal of the IdP.
- The user is requested to authenticate. For example, using two-factor authentication or by entering an authentication code.
- A user is redirected back to the MongoDB client with single-use authorization code.
- The IdP verifies the authorization code, user’s client ID and credentials.
- Upon success, the IdP returns the access and ID tokens to the MongoDB client.
- The MongoDB client uses the access token to access Percona Server for MongoDB.
Benefits¶
The use of OIDC and OAuth 2.0 provides the following benefits:
- streamlines authentication and authorization flow,
- enables you to use modern authentication techniques like 2FA, MFA and others supported by IdP
- improves security as credentials are not sent to nor stored in Percona Server for MongoDB.
- Reduces cross-application risk - access tokens are granted for specific resources using audience claims. If a token is compromised, the token has a limited lifetime and scope to limit access.
Configuration¶
Configure OIDC / OAuth 2.0 authentication and authorization in Percona Server for MongoDB.